Breast cancer recurrence is a concern for many individuals who have undergone treatment for breast cancer. While the initial diagnosis and treatment are overwhelming, the fear of the cancer returning can feel just as daunting. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and ways to reduce the risk of breast cancer recurrence can provide clarity and empower you to take proactive steps toward managing your health.
Raising Awareness About Breast Cancer Recurrence

When breast cancer treatment ends, many people experience a sense of relief. However, for some, the journey isn’t entirely over as the risk of recurrence looms large. Breast cancer recurrence refers to the return of cancer after treatment, either in the same breast or in other parts of the body. With advancements in treatment, many survivors are living longer and healthier lives, but awareness about the risk of cancer recurrence is still essential.
What is Breast Cancer Recurrence?
Breast cancer recurrence can happen months or even years after the initial treatment. It occurs when cancer cells survive after treatment and grow back in the same area (local recurrence) or spread to distant areas of the body (distant recurrence). Understanding the difference between these types of recurrences is critical:
- Local Recurrence: Cancer returns to the same breast or the chest wall where the original cancer was treated.
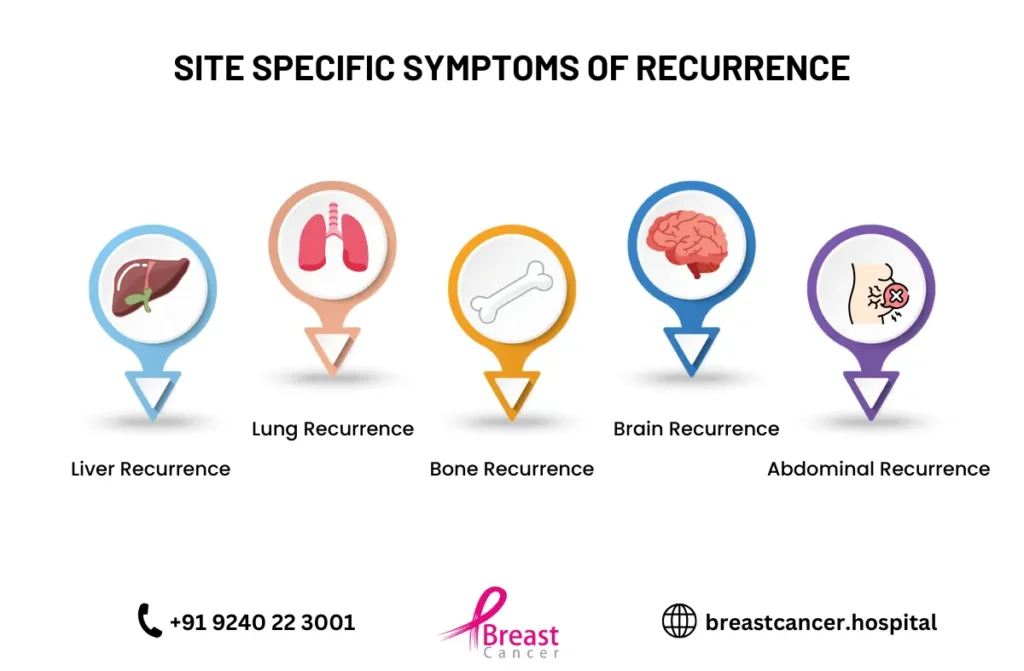
- Distant Recurrence: Cancer spreads to other parts of the body such as bones, lungs, or liver.
Common Signs and Breast Cancer Recurrence Symptoms
It’s crucial to remain vigilant about recognizing Estrogen positive breast cancer recurrence, even after completing treatment. Here are some common symptoms to look out for:
- A new lump in the breast or chest wall: This is often the most common sign of recurrence.
- Changes in the skin texture of the breast: Redness, swelling, or skin that looks dimpled like an orange peel.
- Bone pain: A common symptom when cancer spreads to bones.
- Unexplained weight loss or persistent fatigue: These are often symptoms when cancer has spread to other areas of the body.
- Coughing or difficulty breathing: This can indicate that cancer has spread to the lungs.
What Increases the Risk of Breast Cancer Recurrence?
Understanding the risk of cancer recurrence helps individuals better assess their situation and take necessary precautions. Several factors can increase the likelihood of breast cancer returning:
- Size and Stage of the Original Tumor: Larger tumors and higher-stage cancers generally have a greater chance of recurrence.
- Lymph Node Involvement: If the initial cancer had spread to the lymph nodes, there is a higher risk of it coming back.
- Hormone Receptor Status: Hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer has a lower risk of recurrence than triple-negative breast cancer, but the risk may last longer.
- Type of Treatment: Completing the recommended treatments (surgery, chemotherapy, radiation) significantly reduces recurrence risks. However, skipping or stopping treatments can increase the likelihood of the cancer returning.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, smoking, lack of exercise, and poor diet can contribute to a higher risk of cancer recurrence.
What are the Types of Breast Cancer Recurrence?
Estrogen positive breast cancer recurrence can manifest in three distinct ways:
Local Recurrence:
- This occurs when cancer reappears in the same breast, chest wall, or the scar from the previous surgery.
- Symptoms of breast cancer recurrence locally include:
- A new lump or mass in the treated breast or chest area.
- Unexplained redness, swelling, or skin thickening near the site of the original cancer.
Regional Recurrence:
- Cancer reemerges in nearby lymph nodes, often under the arm, near the collarbone, or in the neck.
- Look out for swelling or lumps in these areas as potential breast cancer recurrence symptoms.
Distant Recurrence:
- Also called metastatic breast cancer, this occurs when the cancer spreads to other parts of the body like bones, lungs, liver, or brain.
- Symptoms may include bone pain, persistent cough, severe headaches, or unexpected weight loss.
By understanding these types, patients and healthcare providers can better utilize tools like the breast cancer recurrence risk calculator to assess individual risks and take preventive measures.
What is the Treatment for Breast Cancer Recurrence?
Surgery
- Local Recurrence: If the cancer is confined to the original area, surgery (e.g., mastectomy or lumpectomy) may be performed to remove the recurrence.
Radiation Therapy
- May be used if not administered previously or directed to new areas of recurrence.
Systemic Therapies
- Hormonal Therapy: For hormone receptor-positive cancers, drugs like tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors may be prescribed.
- Chemotherapy: Targets rapidly dividing cancer cells, particularly for aggressive or distant recurrence.
- Targeted Therapy: Medications like trastuzumab (Herceptin) for HER2-positive cancers or newer targeted drugs.
- Immunotherapy: Helps the immune system fight cancer in certain cases, such as triple-negative breast cancer.
Palliative Care
- Focuses on improving quality of life, especially for metastatic recurrence, by managing symptoms and ensuring comfort.
Clinical Trials
- Access to innovative treatments and drugs for advanced or recurrent cases.
A multidisciplinary team approach is vital to personalize the treatment plan and improve outcomes.
What to Do if You Suspect Breast Cancer Recurrence
If you’re noticing any of the symptoms discussed earlier or have concerns about estrogen-positive breast cancer recurrence, it’s crucial to reach out to your healthcare provider without delay. Detecting a recurrence early can significantly improve treatment effectiveness and overall outcomes.
Here are some steps to take if you’re worried about recurrence:
- Schedule a follow-up appointment: Don’t hesitate to see your doctor if you’re feeling uneasy about new symptoms.
- Request additional screenings: Your doctor may recommend further imaging or biopsies to determine if cancer has returned.
- Join a support group: Emotional support is critical. Join a community of survivors who understand what you’re going through.
- Explore advanced treatments: If recurrence is confirmed, discuss treatment options such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, or targeted therapies.
What Causes Breast Cancer Recurrence?
Breast cancer recurrence happens when cancer returns after initial treatment. Common causes include:
- Microscopic Cancer Cells: Residual cancer cells left behind post-treatment may grow over time, leading to recurrence.
- Incomplete Treatment: If initial treatment didn’t eliminate all cancerous cells, the risk of recurrence increases.
- Cancer Aggressiveness: Some cancers, like triple-negative breast cancer, are more likely to recur due to their aggressive nature.
- Genetic Factors: Mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 can raise the likelihood of recurrence.
- Delayed Diagnosis: If the cancer was initially diagnosed at an advanced stage, recurrence risk is higher.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, and smoking may contribute to cancer returning.
- Regular follow-ups, healthy lifestyle choices, and adherence to prescribed treatments are crucial for minimizing the risk.
What is the Average Time for Breast Cancer Recurrence?
The timeframe for breast cancer recurrence depends on cancer type and treatment received.
- Early Recurrence (within 5 years)
- Common in aggressive cancers like TNBC and HER2-positive breast cancer.
- Often appears in the same breast, nearby lymph nodes, or distant organs.
- Late Recurrence (after 5-10 years)
- Common in estrogen-positive breast cancer recurrence cases.
- Cancer may return in bones, liver, or lungs, requiring long-term monitoring.
Regular checkups and monitoring through a breast cancer recurrence risk calculator can help assess the
What Are the Complications of Recurrent Breast Cancer?
Recurrent breast cancer can lead to a range of physical and emotional challenges:
- Physical Complications
- Pain and swelling at the recurrence site.
- Fatigue and decreased mobility if cancer spreads to bones or joints.
- Organ dysfunction in cases of distant recurrence.
- Emotional and Mental Health Impacts
- Anxiety and depression often accompany the fear of progression.
- Financial strain due to prolonged treatment costs.
- Treatment Side Effects
- Chemotherapy or radiation-related issues like hair loss, nausea, or skin irritation.
Identifying and addressing these complications early can improve the quality of life for patients dealing with breast cancer recurrence symptoms.
Local Breast Cancer Recurrence
Local recurrence specifically refers to cancer reappearing in the area of the original tumor. Recognizing early signs and symptoms is crucial:
- Key Symptoms:
- Firm lumps or nodules under the skin near the surgery site.
- Unusual pain or tenderness in the treated breast or chest wall.
- Changes in skin texture, such as dimpling or puckering.
- Preventive Measures:
- Regular follow-up appointments with your oncologist.
- Mammograms and imaging tests as recommended.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to lower the risk of cancer recurrence.
A breast cancer recurrence risk calculator can help estimate the likelihood of local recurrence, enabling tailored prevention strategies.
Diagnosis and Tests for Breast Cancer Recurrence
Early detection of breast cancer recurrence is crucial for better treatment outcomes. Doctors use various tests to assess if the cancer has returned and to determine the best course of action.
Key Diagnostic Tests for Breast Cancer Recurrence:
- Physical Examination: Doctors check for lumps, swelling, or skin changes in the breast and surrounding areas.
- Mammogram: A specialized X-ray detects changes in breast tissue.
- Ultrasound and MRI: These imaging tests provide detailed views of the breast and lymph nodes.
- CT Scan and PET Scan: Used to check if cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample is taken from the suspicious area to confirm the presence of cancer.
- Blood Tests: Tumor markers and other blood tests help detect signs of recurrence.
Conclusion
Breast cancer recurrence is a possibility, but with proactive measures, a healthy lifestyle, and consistent follow-up care, you can greatly lower the risk. By recognizing the signs, utilizing resources such as a recurrence risk calculator, and understanding factors that contribute to recurrence, you can stay informed and prepared. For those with estrogen-positive breast cancer recurrence, maintaining regular communication with your healthcare team and seeking extra screenings or support when necessary is crucial for ongoing well-being.




