Breast cancer clinical trials play a vital role in the development of new treatments, providing options for those who may not respond well to traditional therapies. By participating in these trials, patients can access groundbreaking therapies and contribute to medical research that could shape the future of breast cancer treatment. This blog will provide an overview of breast cancer clinical trials, their phases, the options available for different stages, and how to access them.
Understanding Breast Cancer Clinical Trials
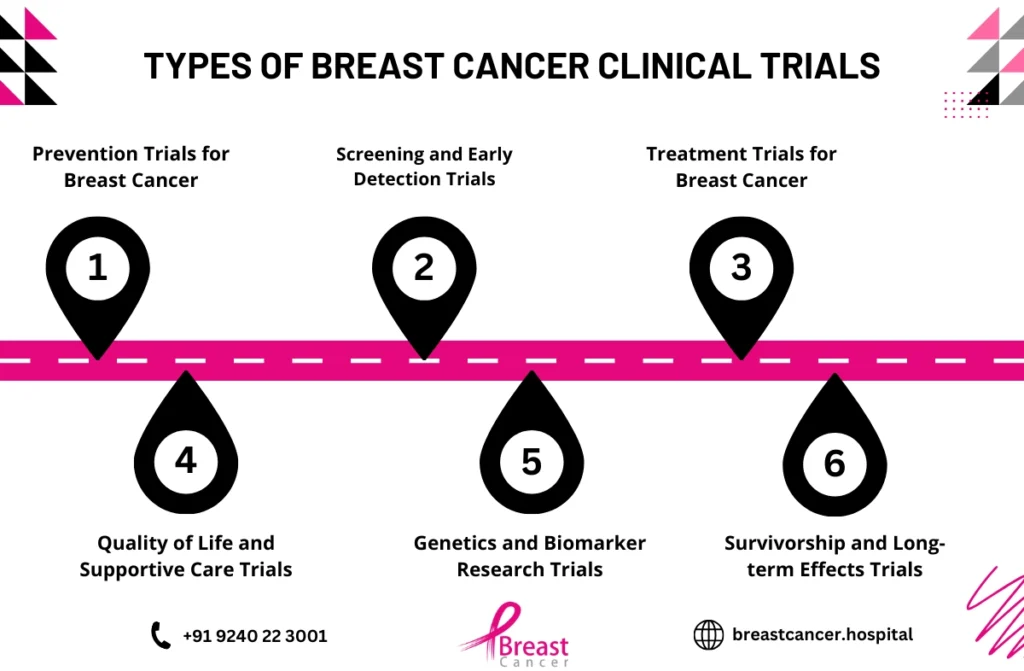
What Are Breast Cancer Clinical Trials?
Breast cancer clinical trials are research studies that test new treatments, therapies, or procedures in a controlled environment to determine their safety and effectiveness. These trials are essential for advancing breast cancer research, providing insights into what treatments work best for different patient groups. Clinical trials are divided into several phases, each focusing on testing different aspects of a potential treatment.
Many current breast cancer clinical trials are focused on exploring targeted therapies, immunotherapies cancer, and personalized medicine, aiming to improve treatment outcomes and quality of life. These trials represent hope for patients, especially those in advanced stages, as they offer new options when traditional treatments have limited effectiveness.
Key Aspects of Breast Cancer Clinical Trials
1. Phases of Breast Cancer Clinical Trials
Breast cancer clinical trials are divided into four main phases, each with specific objectives:
- Phase I: The primary goal is to assess the safety of a new treatment and determine the appropriate dosage. This phase often involves a small group of participants.
- Phase II: In this phase, researchers evaluate the treatment’s effectiveness while continuing to monitor safety.
- Phase III: This phase compares the new treatment to the standard treatment in a larger group of patients to confirm its effectiveness and monitor side effects.
- Phase IV: After approval, Phase IV trials continue to monitor the long-term effectiveness and safety of the treatment in a larger population.
Understanding these phases is essential for patients considering participation in a clinical trial, as each phase offers different levels of safety, monitoring, and potential outcomes. Participating in the early phases involves higher risks, while later phases offer more data on the treatment’s efficacy and side effects.
2. Current Breast Cancer Clinical Trials: Areas of Focus
Current breast cancer clinical trials cover a range of innovative treatments, including immunotherapy, targeted therapies, and hormone treatments. Immunotherapy, for instance, aims to stimulate the immune system to target cancer cells, while targeted therapies focus on specific molecules involved in cancer growth. These trials are designed to personalize treatment, ensuring each patient receives the therapy most likely to work for their unique cancer profile.
Clinical trials are also exploring less invasive treatment options, making them more suitable for those seeking options with minimal side effects. For individuals seeking new solutions or whose cancer has resisted standard treatments, exploring the availability of these current breast cancer clinical trials can open doors to promising therapies and potentially more effective treatments.
3. Clinical Trials for Breast Cancer Stage 4: Options for Advanced Cases
For individuals with advanced or metastatic breast cancer, clinical trials for breast cancer stage 4 provide access to experimental treatments that may extend survival and improve quality of life. These trials focus on treatments tailored to advanced stages, where cancer has spread beyond the breast. Treatments in these trials often include combinations of therapies, novel drugs, or approaches that specifically target metastasized cancer cells.
The focus of these trials is to offer new hope for those whose cancer has not responded to conventional treatments, making them a vital resource for patients in advanced stages. Clinical trials for breast cancer stage 4 are particularly impactful, as they address the unique challenges faced by those with metastatic disease, offering options that could improve both survival rates and quality of life.
4. How to Access Breast Cancer Clinical Trials
Finding and enrolling in breast cancer clinical trials requires guidance from healthcare professionals who can match patients with trials suitable for their specific condition. Many hospitals and cancer centers have research programs dedicated to breast cancer trials, and organizations such as the National Cancer Institute provide resources and databases to help patients find trials.
Patients considering clinical trials should have a thorough discussion with their healthcare provider to understand the potential benefits, risks, and eligibility requirements. This step is crucial to determine if a particular trial is suitable for them and to gain a clear understanding of what participation entails.
The Importance of Clinical Trials for Breast Cancer
Clinical trials for breast cancer treatment are pivotal in discovering new, more effective therapies, improving existing treatments, and understanding how breast cancer responds to different medications and approaches. Participating in a clinical trial allows patients to access the latest treatments while contributing to advancing medical knowledge that could benefit others in the future.
Here’s why current breast cancer clinical trials are so important:
- Innovation in treatment: Clinical trials test cutting-edge therapies that may not yet be available to the general public.
- Improved survival rates: Many breakthroughs in cancer treatment have originated from clinical trials, leading to improved survival rates Clinical trials for breast cancer treatment patients.
- Tailored treatments: Clinical trials often focus on personalized treatments, which are customized to the individual’s genetic makeup or the unique characteristics of their cancer.
For women diagnosed with breast cancer stage 4, clinical trials offer a promising option, especially when conventional treatments have failed or when they are seeking innovative approaches to manage the disease.
Phases of Cancer Treatment Trials
The process of a breast cancer clinical trial is typically conducted in phases, each with a distinct goal. Here’s a breakdown of what these phases involve:
Phase I – Safety and Dosage
- The primary goal of Phase I is to determine the safety of a new treatment.
- This phase focuses on how the body responds to the drug, the correct dosage, and its potential side effects.
- Patients enrolled in Phase I trials often have advanced breast cancer and may have tried other treatments without success.
Phase II – Effectiveness
- In Phase II, researchers focus on whether the treatment is effective against breast cancer.
- This phase also examines side effects and continues to refine the dosage.
Phase III – Comparison
- Phase III trials compare the new treatment to the standard treatment options currently available for breast cancer.
- Large groups of patients participate in these trials, and the results are used to gain regulatory approval for the new treatment.
Phase IV – Post-Marketing Surveillance
- Once a drug or treatment is approved for use, Phase IV trials monitor its long-term effectiveness and safety across a larger population.
Throughout all these phases, clinical trials for breast cancer stage 4 are critical for improving survival rates and extending the quality of life for women diagnosed with advanced cancer.
Clinical Trials Improve Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive form of breast cancer with limited treatment options. However, breast cancer clinical trials are revolutionizing the management of TNBC by introducing innovative therapies. Recent studies indicate that targeted therapies and immunotherapy significantly improve survival rates for TNBC patients.
- Immunotherapy advancements: Trials have shown that checkpoint inhibitors enhance the immune system’s ability to fight cancer.
- Targeted therapies: Drugs focusing on specific genetic markers are increasing remission rates.
- Chemotherapy combinations: Some trials explore chemotherapy with experimental drugs to boost effectiveness.
- Hormonal therapy approaches: Even in TNBC, researchers are exploring hormone-targeting drugs for select patients.
Participation in current breast cancer clinical trials provides access to cutting-edge treatments that may not yet be widely available.
Clinical Trials Using Focused Ultrasound-Induced Thermal Ablation
Breast cancer clinical trials are now incorporating focused ultrasound-induced thermal ablation, a non-invasive method that uses sound waves to destroy cancer cells. This innovative technique is gaining traction due to its precision and minimal side effects.
- Non-invasive approach: Eliminates the need for surgery, reducing recovery time.
- Localized treatment: Targets tumors with high accuracy, preserving surrounding healthy tissue.
- Minimal side effects: Compared to traditional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation.
- Potential combination therapy: Some trials combine ultrasound with immunotherapy to enhance effectiveness.
As part of treatment clinical trials for breast cancer, this approach is being explored to determine its long-term safety and effectiveness.
Clinical Trials Exploring Focused Ultrasound’s Other Biological Mechanisms
Beyond thermal ablation, breast cancer clinical trials are investigating other biological mechanisms of focused ultrasound technology. Researchers are studying how it influences the immune response, drug delivery, and tumor microenvironment.
- Immune system activation: Some trials assess whether focused ultrasound can stimulate the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
- Enhanced drug delivery: Ultrasound waves may improve the penetration of chemotherapy and targeted therapies.
- Tumor microenvironment modification: Research focuses on how ultrasound affects blood vessels and tumor growth.
- Reduced tumor recurrence: Studies aim to determine if this method lowers the risk of cancer returning.
Clinical trials for breast cancer stage 4 are particularly interested in these advancements as they offer potential breakthroughs for late-stage patients.
Treatment Clinical Trials for Breast Cancer
Current breast cancer clinical trials offer a variety of treatment options, from new drug therapies to innovative surgical techniques. These trials aim to find better ways to treat and manage breast cancer, especially for women who have exhausted other treatment options.
Types of Treatment Clinical Trials for Breast Cancer
- Targeted Therapy Trials: These trials focus on drugs that specifically target cancer cells without harming normal cells. They are particularly useful in treating breast cancer stage 4 by stopping cancer cell growth or spreading.
- Immunotherapy Trials: Immunotherapy treatments aim to harness the body’s immune system to fight breast cancer, offering a potentially life-saving option for advanced stages.
- Chemotherapy Trials: Though chemotherapy is a standard treatment, new combinations of chemotherapy drugs are tested in clinical trials to improve effectiveness and reduce side effects.
- Radiation Therapy Trials: These trials explore novel radiation methods to treat localized breast cancer or manage metastasis in advanced cases.
- Combination Therapy Trials: Some clinical trials test the combination of several treatments, such as chemotherapy with immunotherapy, to find the most effective method for treating breast cancer stage 4.
Key Benefits of Participating in Breast Cancer Clinical Trials
- Access to innovative treatments not yet available through standard care.
- Close monitoring from medical experts, ensuring better management of your condition.
- Contribution to scientific progress, helping future breast cancer patients.
- Potential for better outcomes, especially for advanced stages of cancer, where treatment options may be limited.
Why Consider Clinical Trials for Breast Cancer Stage 4?
For those with breast cancer stage 4, clinical trials can provide a new lease on life by offering access to promising therapies not yet available through traditional treatment channels. These trials are critical for improving the prognosis for patients facing advanced cancer, offering potential for prolonged survival and enhanced quality of life.
The Benefits and Risks of Participating in Breast Cancer Clinical Trials
Benefits of Participating in Breast Cancer Clinical Trials
Participating in breast cancer clinical trials offers patients access to cutting-edge treatments that may not yet be widely available. These treatments could be more effective than existing therapies, offering new hope for those with difficult-to-treat breast cancer. Additionally, clinical trials contribute to cancer research, providing data that can help improve future treatment options for others.
For patients with limited treatment options, clinical trials offer a way to receive potential therapies that could positively impact their prognosis and quality of life. In this way, participation can create a sense of empowerment and contribution to advancing breast cancer research.
Potential Risks of Clinical Trials
Like any medical treatment, breast cancer clinical trials come with risks, including potential side effects from new treatments and the possibility that the treatment may not be effective. Early-phase trials carry higher risks as safety and dosage levels are still being evaluated, while later phases may be safer but still have unknowns.
Patients should be aware of these risks and ensure they are fully informed before enrolling in a trial. Thoroughly reviewing trial information, asking questions, and understanding the commitment involved are essential steps for making an informed decision.
Possible Drawbacks of Clinical Trials
While breast cancer clinical trials offer significant benefits, there are potential drawbacks to consider:
- Side effects: New treatments may cause unexpected reactions.
- Eligibility criteria: Not all patients qualify for every trial.
- Placebo risk: Some trials include a placebo group.
- Frequent monitoring: Participants may require additional medical visits.
- Uncertainty: Outcomes are not guaranteed.
Despite these challenges, many patients find current breast cancer clinical trials beneficial, especially when standard treatments have limited effectiveness.
Conclusion
Breast cancer clinical trials provide invaluable opportunities for those seeking new treatment options, particularly for patients with advanced cases or those unresponsive to standard therapies. These trials not only offer potential new paths to recovery but also contribute significantly to breast cancer research, paving the way for future breakthroughs.
For anyone considering clinical trials, consulting with healthcare providers and exploring current breast cancer clinical trials can open doors to innovative therapies. By participating, patients play an active role in advancing breast cancer treatment, potentially benefiting others and themselves. Take the first step by discussing trial options with your healthcare team and exploring the possibilities that clinical trials can offer.




