Chemotherapy for breast cancer plays a crucial role in treating and managing the disease by using powerful medications to target and destroy cancer cells. It is particularly effective in shrinking tumors, improving survival rates, and even acting as preventive chemotherapy for breast cancer. This treatment is especially important for advanced stages, such as chemotherapy for breast cancer stage 4, where it helps to control cancer progression. While chemotherapy can be highly effective, it also has side effects that may impact a patient’s lifestyle. Following a specialized chemotherapy diet chart can help patients maintain strength and manage side effects during treatment.
Why Chemotherapy is Done
Chemotherapy is used for several reasons in breast cancer treatment:
- Shrinking Tumors: Chemotherapy can reduce the size of tumors, particularly when tumors are too large for immediate surgical removal. This is common in neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
- Destroying Cancer Cells: Chemotherapy works by killing cancer cells in the breast and in other parts of the body, including distant organs if cancer has spread. For chemotherapy for breast cancer stage 4, this is crucial in managing the disease.
- Preventing Recurrence: Even after surgery, there could be microscopic cancer cells left in the body. Chemotherapy eliminates these remaining cells to reduce the risk of cancer returning.
In chemotherapy for breast cancer stage 4, the treatment helps control the spread of cancer to distant organs like the liver, bones, and lungs. While chemotherapy may not cure cancer at this stage, it can significantly improve the quality of life and help prolong survival.
When is Chemotherapy Used for Breast Cancer?
Chemotherapy is utilized in different stages of breast cancer depending on the specifics of the case:
- Early-Stage Breast Cancer: In early stages, chemotherapy is usually used as an adjuvant treatment after surgery to destroy any residual cancer cells that are not detectable by imaging tests. This reduces the chances of the cancer returning.
- Advanced-Stage Breast Cancer (Stage 4): For metastatic cancer, where the disease has spread to other parts of the body, chemotherapy for breast cancer stage 4 is often the primary treatment. Its goal is to control cancer growth, alleviate symptoms, and extend life expectancy.
- Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: When tumors are large, chemotherapy is administered before surgery (neoadjuvant therapy) to shrink the tumors. This makes surgery more manageable and less invasive.
Chemotherapy is suitable for both hormone receptor-positive and hormone receptor-negative breast cancer, and it is customized according to the cancer’s subtype and stage.
Chemotherapy as the Primary Treatment for Advanced Breast Cancer
For metastatic or stage 4 breast cancer, chemotherapy becomes a critical treatment. At this stage, cancer has spread from the breast to other organs like the liver, bones, or lungs. The purpose of chemotherapy in this context is not to cure the cancer but to manage its progression, alleviate symptoms, and improve quality of life.For patients with chemotherapy for breast cancer stage 4, the focus is on palliative care. Chemotherapy helps control cancer growth and can sometimes reduce tumor size, providing symptom relief. While chemotherapy may not cure the cancer, it significantly improves survival rates and can help patients live longer with a better quality of life.
Chemotherapy Drugs Used for Breast Cancer
Several chemotherapy drugs are widely used in the treatment of breast cancer. These drugs are often combined to maximize effectiveness. Some common chemotherapy drugs for breast cancer include:
- Doxorubicin (Adriamycin): A potent drug used for aggressive breast cancer types, including chemotherapy for breast cancer stage 4. It works by damaging the DNA inside cancer cells, preventing them from replicating.
- Cyclophosphamide: This drug is frequently combined with other chemotherapy agents. It works by damaging the cancer cells’ DNA and preventing cell division.
- Taxanes (Paclitaxel, Docetaxel): These drugs prevent cancer cells from dividing, stopping cancer growth. They are commonly used in both early and advanced stages of breast cancer, including chemotherapy for breast cancer stage 4.
- Capecitabine (Xeloda): This is an oral chemotherapy medication that is converted into a more potent form inside the body. It is commonly used for patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer and is particularly effective in chemotherapy for breast cancer stage 4.
The combination of chemotherapy drugs used depends on the cancer’s specific characteristics, its stage, and the patient’s health status.
How is Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer Given?
Chemotherapy can be delivered in two primary ways:
- Intravenous (IV) Infusion: The most common method, chemotherapy drugs are delivered directly into the bloodstream through a catheter or IV line. This allows the drugs to quickly circulate throughout the body.
- Oral Pills: Some chemotherapy drugs, such as Capecitabine, are available in pill form and can be taken at home. While more convenient, oral chemotherapy is not suitable for all patients and may be used in combination with IV chemotherapy.
The frequency and duration of chemotherapy cycles depend on the type of cancer and the drugs being used. For chemotherapy for breast cancer stage 4, the treatment regimen may last several months, with breaks in between to allow the body time to recover.Chemotherapy may be administered in an outpatient setting or in a hospital, depending on the intensity of the treatment and the drugs used.
3 Major Purpose of Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer
Three major purposes of chemotherapy in breast cancer treatment are:
Primary Treatment: Chemotherapy can be used as the primary treatment for breast cancer, especially in cases where the cancer has spread beyond the breast or lymph nodes. By targeting and killing cancer cells throughout the body, chemotherapy aims to shrink tumors, reduce the risk of recurrence, and improve overall survival rates.
Adjuvant Therapy: Chemotherapy is often used as adjuvant therapy after surgery to remove the tumor. This preventive approach helps to kill any remaining cancer cells that may not have been removed during surgery, reducing the risk of cancer recurrence and improving long-term outcomes for patients.
Neoadjuvant Therapy: In some cases, chemotherapy may be administered before surgery as neoadjuvant therapy. The goal of this approach is to shrink the tumor so that it is easier to remove surgically. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy can also help assess the tumor’s response to treatment and guide further therapy decisions.
What Are Common Types of Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer?
The type of chemotherapy used depends on the cancer’s stage, subtype, and patient health. Here are the commonly used options:
Anthracyclines
- Examples: Doxorubicin (Adriamycin), Epirubicin.
- Effective against aggressive types of breast cancer.
Taxanes
- Examples: Paclitaxel (Taxol), Docetaxel (Taxotere).
- Often used in combination therapies to prevent cancer cell division.
Platinum-based drugs
- Examples: Cisplatin, Carboplatin.
- Effective for triple-negative breast cancer.
Anti-metabolites
- Example: Capecitabine (Xeloda).
- Used for advanced or metastatic breast cancer.
Common Drugs Used in Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer
Some common chemotherapy drugs for breast cancer include
- Doxorubicin (Adriamycin): Damages the DNA of cancer cells to induce cell death.
- Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan): Interferes with the growth and spread of cancer cells.
- Paclitaxel (Taxol): Disrupts cell division by targeting microtubules.
- Docetaxel (Taxotere): Inhibits cell division by targeting microtubules.
- Fluorouracil (5-FU): Inhibits DNA and RNA synthesis in cancer cells.
- Gemcitabine (Gemzar): Interferes with DNA replication to cause cancer cell death.
- Carboplatin: Damages DNA in cancer cells to inhibit cell growth.
Possible Side Effects of Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer
While chemotherapy is effective, it can cause side effects. These side effects may vary based on the patient and the drugs used. Common side effects of chemotherapy include:
- Nausea and Vomiting: Chemotherapy can irritate the digestive system, leading to nausea. Anti-nausea medications are often prescribed to alleviate these symptoms.
- Fatigue: Fatigue is a common and significant side effect that can limit daily activities. It results from the toll chemotherapy takes on the body’s energy reserves.
- Hair Loss: Most chemotherapy drugs cause temporary hair loss, which typically begins a few weeks after treatment starts.
- Increased Risk of Infections: Chemotherapy suppresses the immune system, making patients more vulnerable to infections. Regular monitoring is essential to prevent serious infections.
- Mouth Sores and Digestive Issues: Sores in the mouth and digestive issues like diarrhea or constipation are common, as chemotherapy can affect the gastrointestinal system.
A chemotherapy diet chart can be helpful in managing side effects by ensuring the patient receives adequate nutrition, which is crucial to support the immune system and overall recovery.
Menstrual Changes and Fertility Issues

Chemotherapy can lead to significant changes in menstrual cycles, particularly for women undergoing chemotherapy for breast cancer stage 4, where the treatment tends to be more aggressive. Many women experience temporary or permanent infertility due to the effects of chemotherapy on the ovaries.
For women wishing to preserve fertility, options like egg freezing or ovarian tissue cryopreservation are available before treatment. These options should be discussed with a fertility specialist before chemotherapy begins.
Risks of Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer
While chemotherapy is an effective treatment, it comes with risks:
- Weakened Immune System: Chemotherapy can lower white blood cell counts, weakening the immune system and increasing the risk of infections.
- Organ Damage: Some chemotherapy drugs can damage organs like the heart, liver, and kidneys. Close monitoring is required to manage these risks.
- Secondary Cancers: In rare cases, chemotherapy may increase the risk of developing secondary cancers later in life.
A chemotherapy diet chart is one way to mitigate some of these risks by providing essential nutrients to support the immune system and organ health.
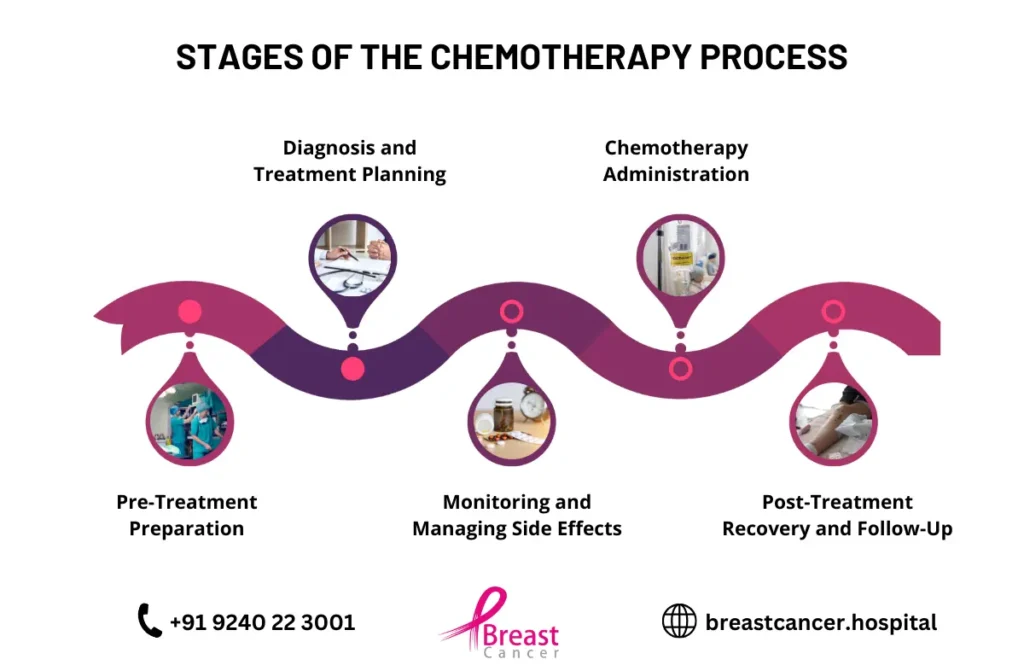
How You Prepare for Chemotherapy
Before chemotherapy begins, patients undergo medical assessments, including blood tests and imaging, to determine their overall health and readiness for treatment. It is essential to also prepare emotionally, as chemotherapy can be physically and psychologically challenging.
Doctors may recommend lifestyle changes, such as following a balanced diet, staying active, and managing stress. Mental health support, including therapy and counseling, is also vital to help patients cope with the emotional stress of chemotherapy.
Take Steps to Improve Your Overall Health
During chemotherapy, maintaining good health is crucial. Following a chemotherapy diet chart ensures that patients are eating well to maintain their energy levels and support their immune system. Regular light exercise, such as walking, can also help manage fatigue and keep muscles strong.
Mental health support, such as joining support groups or seeking therapy, can help patients cope with the emotional burden of chemotherapy.
What You Can Expect During the Course of Chemotherapy
Throughout chemotherapy, patients will undergo several cycles of treatment. Doctors will monitor progress, adjusting treatment plans as necessary to ensure optimal effectiveness. Patients will receive guidance on how to manage side effects, including tips on nutrition, hydration, and stress management.
Chemotherapy as the Primary Treatment for Advanced Breast Cancer
For patients with stage 4 breast cancer, chemotherapy often becomes the cornerstone of treatment. At this stage, cancer may have spread to other organs, requiring systemic therapies to manage the disease and improve quality of life.
Key points about chemotherapy for breast cancer stage 4:
- Combination therapy: Often involves multiple drugs to increase efficacy.
- Targeted approach: Some treatments are designed to target specific cancer cell receptors.
- Palliative care: In addition to shrinking tumors, it helps alleviate symptoms like pain or difficulty breathing.
Chemotherapy Before Surgery for Breast Cancer
Also known as neoadjuvant chemotherapy, this approach helps shrink the tumor before surgical removal, making breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) more viable. Key benefits include:
- Reducing tumor size: Enhances the chances of a successful surgery.
- Assessing drug effectiveness: Helps oncologists determine the cancer’s response to specific chemotherapy drugs.
- Targeting hidden cancer cells: Eliminates undetectable cancer cells, reducing the risk of recurrence.
- Enhancing long-term survival rates: Especially beneficial for aggressive cancer types.
What Are the Benefits of Chemotherapy?
Chemotherapy for breast cancer offers several advantages:
- Eliminates Cancer Cells: Reduces or eliminates cancer before or after surgery.
- Prevents Recurrence: Used in preventive chemotherapy for breast cancer to minimize future risks.
- Controls Advanced Cancer: Helps manage chemotherapy for breast cancer stage 4 effectively.
- Combination Therapy: Enhances the effectiveness of radiation or hormone treatments.
- Improves Quality of Life: Reduces pain and symptoms associated with breast cancer.
A proper chemotherapy diet chart supports recovery and helps manage treatment-related side effects.
Chemotherapy Diet Chart
Maintaining a healthy diet during chemotherapy for breast cancer is essential for supporting your body’s strength, managing side effects, and promoting overall well-being. A chemotherapy diet chart can help you make nutritious choices that support your treatment and recovery.
- Focus on eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to provide essential nutrients and support immune function.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day, aiming for at least eight glasses per day.
Managing Side Effects and Coping Strategies
Chemotherapy for breast cancer can cause a range of side effects, which vary depending on the specific drugs used, dosage, and individual factors. Understanding these potential side effects and implementing coping strategies can help you navigate treatment more effectively.
Common Side Effects of Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer:
- Nausea and vomiting: Medications can help manage nausea and vomiting, and dietary changes such as eating small, frequent meals and avoiding spicy or greasy foods may also help.
- Hair loss: Hair loss is a common side effect of chemotherapy, but it is usually temporary. Consider exploring options such as wigs, scarves, or hats to help maintain your confidence and self-esteem.
- Fatigue: Fatigue is another common side effect that can impact daily activities. Prioritize rest, conserve energy, and ask for help when needed to manage fatigue effectively.
Conclusion
Chemotherapy for breast cancer is a critical component of treatment for many patients, whether for shrinking tumors, controlling metastatic disease, or preventing recurrence. Although chemotherapy comes with side effects, these can be managed with proper care, medications, and lifestyle adjustments. A chemotherapy diet chart is one way to support the body during treatment, helping patients maintain strength and improve overall outcomes.Collaboration with a healthcare team is key to developing a personalized treatment plan tailored to the patient’s unique needs. With proper support, patients can navigate their chemotherapy journey with confidence and the knowledge that they have the tools to fight breast cancer effectively.