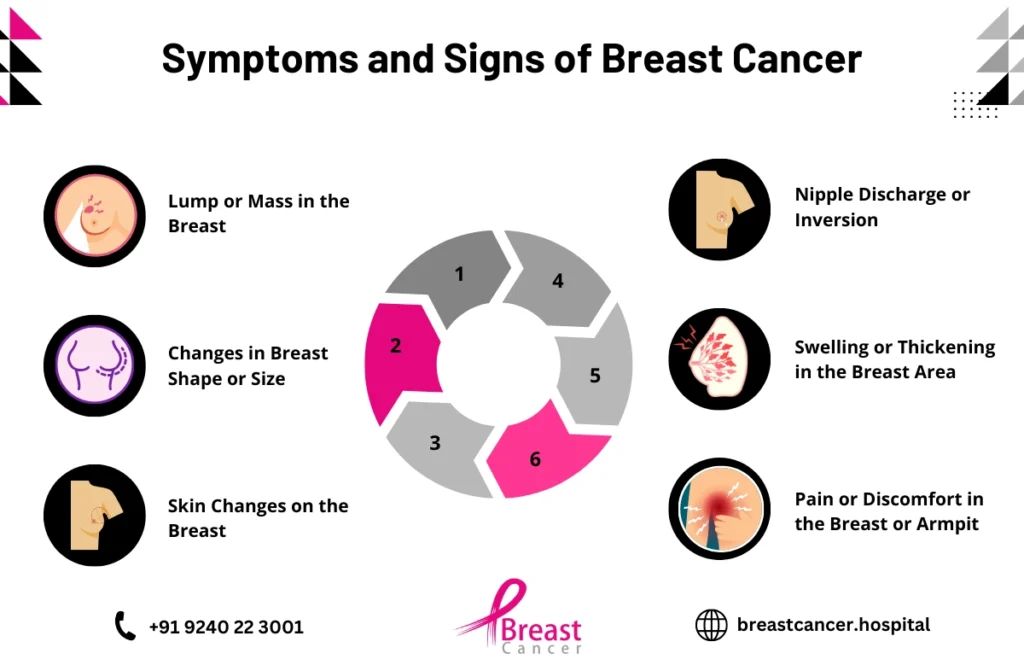
“Symptoms and signs of breast cancer” can vary widely, and understanding them is essential for early detection and effective treatment. Breast cancer affects people of all backgrounds, and while some symptoms are common, others can be more subtle. In this post, we’ll explore key breast cancer symptoms, early warning signs, and how these symptoms may differ among various groups and stages.
Understanding the Complications of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer can lead to a variety of complications, especially if it goes undiagnosed or untreated for too long. Some of the complications include:
- Metastasis: Breast cancer can spread to other parts of the body, such as the bones, liver, lungs, or brain.
- Pain and Discomfort: Advanced stages of breast cancer may cause severe pain in the breasts or other affected areas.
- Lymphedema: When lymph nodes are removed or affected by cancer, it can cause fluid retention and swelling in the arm or other areas.
- Emotional and Psychological Impact: The diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer can lead to anxiety, depression, and emotional distress.
Metastatic Breast Cancer Symptoms
Metastatic breast cancer occurs when cancer cells spread from the breast to other parts of the body, such as the bones, liver, lungs, or brain. Stage 4 breast cancer end of life symptoms may be different from early-stage symptoms, as the disease has spread extensively. Common symptoms include:
- Bone Pain: Pain in the bones, particularly in the back, hips, or ribs, which may indicate metastasis to the bones.
- Difficulty Breathing: Shortness of breath or a persistent cough could suggest that the cancer has spread to the lungs.
- Neurological Symptoms: Headaches, dizziness, or vision changes may indicate that the cancer has spread to the brain.
- Fatigue and Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss, along with extreme fatigue, could be a sign of metastatic breast cancer.
Understanding these symptoms is crucial for patients and their families as they can help guide treatment decisions and palliative care options.
Diagnosis and Tests for Breast Cancer
When doctors suspect breast cancer, they will often conduct a series of tests to confirm the diagnosis and determine the stage of the cancer. Here are the common diagnostic methods used:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) – An MRI may be recommended in certain cases, especially for high-risk patients.
- Mammogram – This is the most common imaging test used to detect breast cancer. It can identify abnormalities that may not be felt during an examination.
- Ultrasound – An ultrasound may be used to further examine a lump or abnormality found during a mammogram.
- Biopsy – If a suspicious mass is found, a biopsy is performed to remove tissue samples for testing.
Common Early Warning Signs
- Breast Pain or Discomfort: While not always a primary sign, some early breast cancer cases present with pain or discomfort in the breast area. Persistent pain should be evaluated, particularly if it’s isolated to one breast.
- Lump in the Armpit: Swollen lymph nodes in the armpit can be an early warning signs of breast cancer. Lymph nodes are part of the body’s immune system and may become swollen if cancer cells start to spread.
- Color Changes in the Breast: A sudden change in breast color, such as redness or a purple hue, can be a warning sign. This symptom is often associated with inflammatory breast cancer, a rare but aggressive form of the disease.
What Is a Normal Breast?
Before identifying abnormalities, it’s essential to understand what a normal breast looks and feels like.
- Breasts come in various shapes and sizes, and slight asymmetry is normal.
- The texture of breast tissue can change with age, menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause.
- Normal breasts may have some lumpiness due to glandular tissue, especially before menstruation.
- Nipples should be symmetrical without unusual discharge (unless breastfeeding or pregnant).
Understanding these aspects can help distinguish between normal variations and potential warning signs of breast cancer.
Symptoms of Different Breast Cancer Types
Breast cancer manifests in several different types, each with its symptoms. Here are some of the main types of breast cancer and their associated symptoms:
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS)
- Breast Cancer Symptoms in Black Females: In some cases, breast cancer symptoms in black females may present differently, with DCIS being more aggressive in this demographic. Symptoms include:
- A lump in the breast
- Bloody discharge from the nipple
- Skin changes around the nipple
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC)
IDC is the most common type of breast cancer, where cancer cells spread beyond the milk ducts into surrounding tissue. Symptoms include:
- A hard, irregular lump in the breast
- Skin dimpling or redness
- Swelling or pain in the breast
Inflammatory Breast Cancer (IBC)
IBC is an aggressive form of breast cancer, often diagnosed at a later stage. Symptoms of IBC may include:
- Red, swollen, and warm breast
- Thickened skin with an “orange peel” appearance
- Rapid changes in the size and shape of the breast
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC)
This form of cancer lacks the three receptors known to fuel most breast cancer growth (estrogen, progesterone, and HER2). Symptoms include:
- A fast-growing, painless lump
- More likely to be diagnosed in younger women
- Higher risk of recurrence after treatment
Symptoms and Signs of Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Stage 4 breast cancer is the most advanced stage, where cancer has spread to other parts of the body. “Stage 4 breast cancer end of life symptoms” vary and often include systemic symptoms as the body is affected beyond the breast.
Common End-of-Life Symptoms
- Bone Pain: Breast cancer that has spread to the bones often results in significant pain, particularly in areas like the hips, spine, and legs.
- Difficulty Breathing: If cancer spreads to the lungs, it can lead to shortness of breath and persistent coughing.
- Neurological Symptoms: Cancer spread to the brain can cause headaches, confusion, or seizures, which are more common in advanced stages.
Supportive Care Options
Palliative care plays an essential role for those with stage 4 breast cancer, focusing on symptom relief and improving quality of life. Treatments, including medications, physical therapy, and emotional support, help manage symptoms, giving patients comfort and dignity during advanced stages of the disease.
Breast Cancer Symptoms in Black Females
“Breast cancer symptoms in black females” may differ slightly due to genetic and biological factors. Studies show that Black women are more likely to develop aggressive types of breast cancer at younger ages, making awareness even more crucial in this demographic.
Differences in Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Higher Incidence of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Black women are more likely to develop triple-negative breast cancer, which lacks certain receptors, making it more challenging to treat.
- Earlier Age of Onset: Black females often experience breast cancer at a younger age than white females, highlighting the importance of self-examinations and early screening.
- More Aggressive Symptoms: Breast cancer in Black females may progress more quickly, with symptoms such as larger lumps or more pronounced skin changes appearing earlier in the disease course.
Encouraging Early Detection in Black Females
Routine screenings and early awareness campaigns are particularly beneficial for Black women, who may be at risk of developing more aggressive breast cancer forms. Health providers are encouraged to inform patients about specific risk factors and the importance of early detection.
Complications of Breast Cancer Surgery
While breast cancer surgery is a lifesaving procedure, it may have some complications:
- Lymphedema (Swelling in the Arm or Chest): Lymph node removal can cause fluid buildup, leading to swelling.
- Pain and Nerve Damage: Some women experience chronic pain or tingling due to nerve damage.
- Infection at the Surgical Site: Redness, swelling, and discharge may indicate an infection requiring medical attention.
- Changes in Breast Appearance: Partial or full mastectomy can lead to emotional and psychological challenges.
- Limited Arm Movement: Some women have difficulty lifting their arms after surgery.
What Causes Breast Cancer?
Understanding the causes of breast cancer in unmarried girl is vital for prevention and awareness. While the exact causes of breast cancer in unmarried girl remains unclear, several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing breast cancer. Some of these include:
- Genetic Mutations: Inherited mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 can significantly increase the risk of breast cancer.
- Hormonal Factors: Prolonged exposure to estrogen, early menstruation, late menopause, or hormone replacement therapy can increase risk.
- Age: The risk of developing breast cancer increases with age, particularly after 50.
- Family History: A family history of breast cancer can elevate the likelihood of developing the disease.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, alcohol consumption, poor diet, and lack of physical activity can contribute to an increased risk of breast cancer.
Risk and Prevention
Knowing the causes of breast cancer and understanding how to prevent it is crucial for maintaining breast health. While some risk factors cannot be controlled, others can be managed through lifestyle changes and proactive measures.
How to Avoid Breast Cancer
Preventing breast cancer involves a combination of awareness, healthy lifestyle choices, and regular screenings. Here are some key actions you can take:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight, especially after menopause, increases the risk of developing breast cancer. Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake is a known risk factor for breast cancer. Limit alcohol to no more than one drink per day.
- Breastfeed if Possible: Breastfeeding for several months has been shown to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer in women.
- Avoid Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Long-term use of combined hormone therapy can increase the risk of breast cancer.
Conclusion
Being aware of the “symptoms and signs of breast cancer” can make a significant difference in early detection and treatment outcomes. Recognizing changes such as lumps, skin alterations, and nipple discharge, and understanding how these symptoms can present differently among individuals, allows for proactive health management. If you or a loved one notices any concerning changes, consult a healthcare provider to ensure early intervention. Staying informed is a powerful tool in the fight against breast cancer.