Pain in breast and back is a common concern for many individuals and can stem from various reasons, ranging from simple muscle strain to more serious health issues like breast cancer. While occasional pain may not be alarming, persistent or severe discomfort could be linked to more significant conditions. Understanding the connection between pain in breast and back, especially its association with breast cancer, can help individuals take timely action for diagnosis and treatment. In this blog, we’ll explore the possible causes, symptoms, and treatments related to this pain, including how breast cancer may play a role.
Causes of Pain in Breast and Back
Pain in breast and back can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. It may be localized or radiate to other areas, depending on the underlying cause. While hormonal changes, poor posture, or physical strain are common reasons, the possibility of serious conditions like breast cancer should not be ignored.
Possible Causes of Pain in Breast and Back:
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can cause breast tenderness and mild back pain.
- Injury or Strain: Physical injuries or strain from poor posture can lead to discomfort in both areas.
- Breast Cancer: Pain in breast and back can sometimes signal breast cancer, especially when accompanied by other symptoms like lumps or swelling.
Symptoms of Pain in Breast and Back
Identifying the symptoms associated with pain in breast and back is crucial for understanding its cause. While some symptoms are mild and temporary, others may indicate serious underlying conditions.
Common Symptoms:
- Breast Pain:
- Tenderness, burning, or a dull ache in one or both breasts.
- Persistent pain that does not fluctuate with the menstrual cycle.
- Visible changes in breast skin or nipple discharge.
- Back Pain:
- Chronic or sharp pain in the upper or lower back.
- Stiffness or discomfort while sitting or lying down.
- Pain that worsens over time, despite rest or medication.
If these symptoms persist or worsen, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
Breast Cancer and Back Pain: Are They Linked?
Breast cancer and back pain are often linked when the disease spreads to surrounding tissues or bones. Breast cancer and back pain may not always appear together in the early stages, but they can co-occur when cancer progresses or metastasizes.
Key Points About Breast Cancer and Back Pain:
- Advanced breast cancer often spreads to the bones, causing persistent back pain.
- Pain may start in the spine and radiate to other areas.
- Early detection of breast cancer and back pain can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
If you experience consistent back pain along with other symptoms like breast changes or fatigue, consult your doctor immediately.
Is Lower Back Pain a Warning Sign of Breast Cancer?
Lower back pain is not always associated with breast cancer but can be a warning sign in some cases, particularly when the disease metastasizes. Lower back pain breast cancer metastasis occurs when cancer spreads to the lower spine, causing discomfort and other related issues.
When to Suspect Breast Cancer in Lower Back Pain:
- The pain is deep, persistent, and does not improve with rest or common remedies.
- It is accompanied by other symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, or changes in breast appearance.
- Imaging tests reveal bone abnormalities or lesions.
While lower back pain breast cancer metastasis is not a definitive diagnosis, it is a condition that requires prompt medical evaluation.
Breast Cancer and Back Pain: What to Know?
When breast cancer progresses to an advanced stage, it often spreads to the bones, including the lower spine. This condition, known as lower back pain breast cancer metastasis, can cause chronic pain and reduced mobility.
Lower Back Pain in Breast Cancer Spread
- Pain that worsens at night or during physical activity.
- Stiffness and swelling around the affected area.
- Weakness or numbness in the legs due to spinal compression.
Steps to Address Lower Back Pain Breast Cancer Metastasis:
- Regular imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, can help confirm the diagnosis.
- Pain management through medications, physical therapy, or alternative therapies can improve quality of life.
- Early intervention is key to managing symptoms and preventing further complications.
Back Pain From Breast Cancer Treatment:
Many individuals undergoing breast cancer treatment experience side effects, one of which is back pain. Back pain from breast cancer treatment is a common issue that arises due to the nature of therapies such as surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation.
Causes of Back Pain From Breast Cancer Treatment:
- Surgical Recovery: Procedures like mastectomies or reconstruction surgeries can strain back muscles.
- Radiation Therapy: Inflammation of tissues near the spine can cause discomfort.
- Chemotherapy: Weakening of bones and muscles can lead to chronic pain.
Managing Back Pain From Breast Cancer Treatment:
- Physical therapy can help restore mobility and reduce stiffness.
- Medications such as pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs can provide relief.
- Gentle exercises like yoga or stretching can strengthen muscles and alleviate discomfort.
Discussing pain management options with your doctor can help you navigate the challenges of back pain during treatment.
Managing Pain in Breast and Back Effectively
Effective management of pain in breast and back requires addressing both the symptoms and their root causes. Whether the pain is related to daily habits, injury, or breast cancer, there are several strategies to alleviate discomfort.
Tips to Manage Pain in Breast and Back:
- Maintain Good Posture: Sit and stand with a straight spine to reduce strain on the back.
- Use Supportive Clothing: Wear a properly fitted bra to minimize breast discomfort.
- Incorporate Regular Exercise: Light physical activity can strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
- Consult a Specialist: Persistent pain may require professional evaluation for appropriate treatment.
Preventing Back Pain During Breast Cancer Treatment
Preventing back pain during breast cancer treatment involves adopting proactive measures to reduce strain and maintain strength. Taking steps early can significantly minimize the risk of back pain from breast cancer treatment.
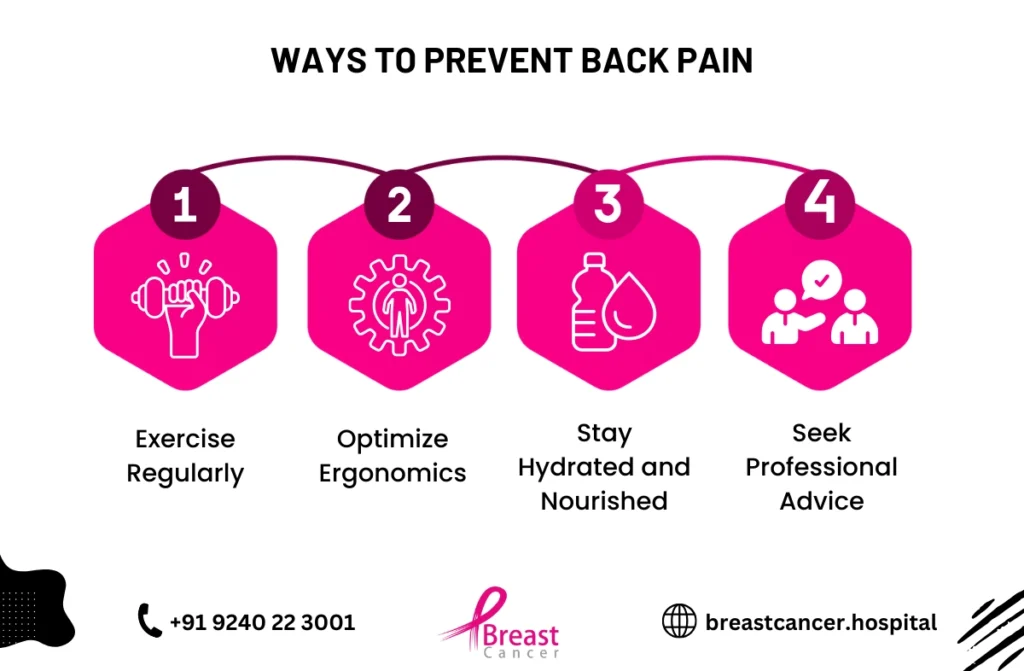
Ways to Prevent Back Pain:
- Exercise Regularly: Gentle activities like walking or stretching help keep muscles active and prevent stiffness.
- Optimize Ergonomics: Use chairs with proper lumbar support and avoid slouching.
- Stay Hydrated and Nourished: Proper hydration and a nutrient-rich diet can promote bone health.
- Seek Professional Advice: Work with a physiotherapist to develop a back care routine.
By following these tips, patients can reduce discomfort and improve their overall quality of life during treatment.
Diagnosis of Pain in Breast and Back
Accurate diagnosis is essential to determine whether pain in breast and back is linked to breast cancer or another condition. A combination of tests and medical history reviews helps healthcare professionals identify the cause.
Diagnostic Methods for Pain in Breast and Back:
- Mammograms and Ultrasounds: These imaging tests help detect abnormalities in the breast tissue.
- Bone Scans or MRIs: To check for signs of bone metastasis or other spine-related issues.
- Blood Tests: Markers like calcium levels or specific proteins can indicate bone involvement.
Timely diagnosis can ensure early intervention and prevent complications related to breast cancer or other causes of pain in breast and back.
Conclusion
Pain in breast and back is a concern that should never be overlooked, especially when it could be linked to serious conditions like breast cancer. While not all pain indicates cancer, understanding the relationship between pain in breast and back and breast cancer is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. Persistent or unusual pain should be promptly evaluated to rule out conditions like lower back pain breast cancer metastasis or side effects from treatment.




