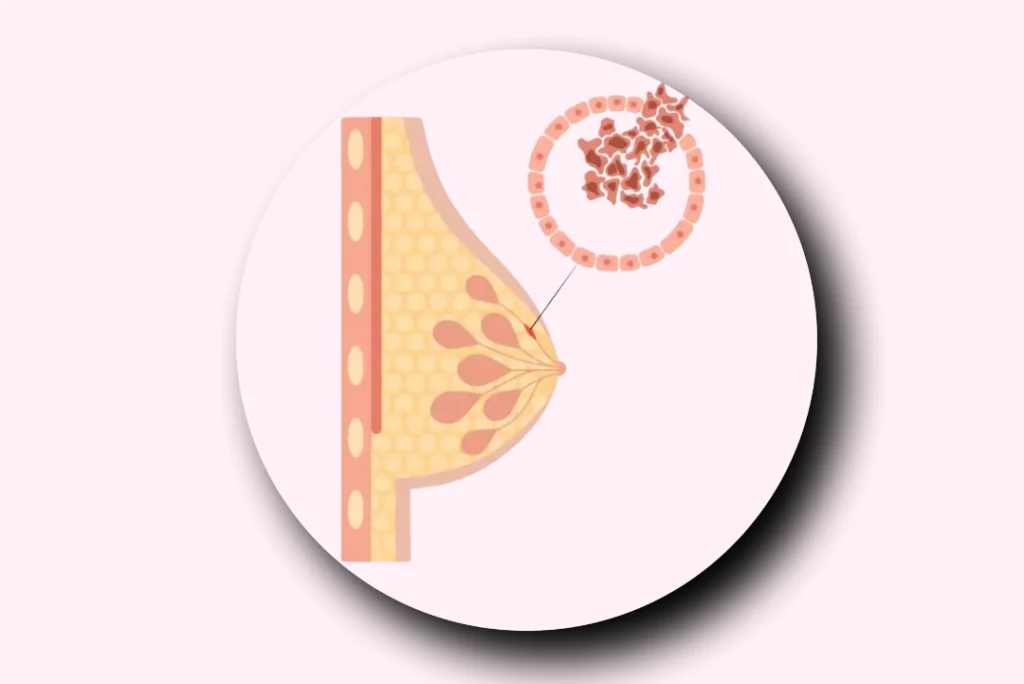
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS) is an early, non-invasive form of breast cancer where abnormal cells develop within the milk ducts but haven’t spread to nearby tissue. While not immediately life-threatening, DCIS requires prompt attention to prevent progression into invasive breast cancer. Early detection, often through routine mammograms, plays a crucial role in successful treatment. Understanding your options for treatment from lumpectomy and mastectomy to hormone therapy empowers you to make informed decisions. This guide will help you navigate the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment choices for DCIS, ensuring you take the necessary steps for a positive outcome.
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Treatment in Chennai
When faced with a diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ treatment in chennai, it’s natural to feel overwhelmed. As a non-invasive breast cancer in chennai, DCIS is a condition that requires timely intervention to prevent progression. This blog post will guide you through the key aspects of DCIS, including causes, symptoms, and treatment options. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding and confidence to make informed decisions about your treatment.
What is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS)?
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS) is an early-stage, non-invasive breast cancer in chennai that occurs when abnormal cells are found in the lining of the milk ducts of the breast. The term “in situ” means these cancerous cells have not spread into surrounding breast tissue, which makes DCIS highly treatable if caught early. It’s important to note that while DCIS is not immediately life-threatening, if left untreated, it can develop into invasive breast cancer.
How Common is DCIS?
DCIS is becoming increasingly common, especially with improved breast cancer screening techniques.
- It accounts for about 20% of all new breast cancer diagnoses globally.
- The number of DCIS cases has risen due to increased mammography screenings.
- The condition is most commonly diagnosed in women over 50 years of age, but younger women can also develop DCIS.
In Chennai, breast cancer awareness programs and advanced diagnostic tools have significantly improved Ductal Carcinoma in Situ symptoms in Chennai detection.
Understanding the Importance of Early Detection
Early detection is critical for successful ductal carcinoma in situ treatment in chennai. DCIS is often detected during routine mammograms, as it usually doesn’t present obvious ductal carcinoma in situ symptoms. Regular screenings are especially important for those at a higher risk of developing non-invasive breast cancer in chennai, including individuals with a family history of breast cancer.
What are the Complications of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ?
While DCIS is not life-threatening on its own, untreated cases may progress to Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) in Chennai, which can spread beyond the breast.
Potential Complications Include:
- Progression to IDC – Untreated DCIS can develop into invasive cancer, affecting nearby lymph nodes and organs.
- Recurrence – Even after treatment, there is a risk of DCIS returning or becoming invasive.
- Surgical and Radiation Side Effects – Breast-conserving surgery or mastectomy can lead to pain, scarring, or lymphedema.
- Psychological Impact – A cancer diagnosis can cause anxiety, depression, and stress.
Early Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Treatment in Chennai can help mitigate these complications and ensure better long-term outcomes.
Symptoms of DCIS
DCIS often shows no symptoms, and it is usually detected during a mammogram screening. However, some individuals may experience signs that could indicate the presence of DCIS. These symptoms include:
- A lump in the breast.
- Changes in the shape or size of the breast.
- Nipple discharge, often clear or bloody.
- Redness or scaling of the skin on the nipple or breast.
Although these symptoms may not always be caused by DCIS, they should prompt immediate medical evaluation. Early detection improves treatment outcomes and reduces the chances of cancer progression.
- Symptoms of DCIS are often subtle or absent.
- Regular mammograms are essential for detecting DCIS early.
- Any changes in the breast or nipple should be examined by a healthcare professional.
Treatment Options for DCIS
When it comes to Ductal Carcinoma in Situ treatment in chennnai, there are multiple options available depending on the patient’s unique case. Treatment aims to remove the abnormal cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Surgery: The most common treatment for DCIS is surgery. This may involve a lumpectomy, which removes only the affected tissue, or a mastectomy, which removes the entire breast. A lumpectomy is often followed by radiation therapy to ensure all cancerous cells are eradicated.
- Radiation Therapy: Following surgery, radiation therapy may be recommended to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. This therapy reduces the chances of DCIS recurrence or its progression to invasive cancer.
- Hormonal Therapy: Hormonal therapy might be advised for women whose DCIS is hormone receptor-positive. This treatment helps reduce the risk of developing breast cancer in the future by blocking the effects of estrogen, which can promote cancer growth.
Success Rate of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Treatment in Chennai
DCIS has an excellent prognosis, with almost a 100% survival rate when treated appropriately. The treatment success rate depends on factors such as:
- Early Detection – The earlier DCIS is identified, the better the treatment outcomes.
- Personalized Treatment Plans – Combining surgery, radiation, and hormone therapy reduces the risk of recurrence.
- Post-Treatment Monitoring – Regular check-ups ensure any abnormalities are detected early.
Thanks to advancements in medical technology, Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Treatment in Chennai offers world-class treatment options for patients.
Causes of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS)
The exact cause of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is not fully understood, but research has identified several factors that contribute to its development. Understanding these causes can help in taking preventive measures and making informed decisions about ductal carcinoma in situ treatment in chennai.
- Genetic Mutations: Mutations in certain genes, like BRCA1 and BRCA2, significantly increase the risk of developing DCIS. Women who inherit these genetic mutations are at a higher risk of both DCIS and other forms of breast cancer.
- Hormonal Influence: Prolonged exposure to hormones such as estrogen has been linked to an increased likelihood of developing DCIS. Women who experience early menstruation, late menopause, or undergo hormone replacement therapy are at higher risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Certain lifestyle choices, including poor diet, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity, can raise the risk of breast cancer, including non-invasive breast cancer like DCIS. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for reducing risk.
Understanding these causes enables early detection and a proactive approach to ductal carcinoma in situ treatment in chennai.
How is Breast Cancer Treated in Chennai?
Treating Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) requires a tailored approach based on the individual case. Various treatments, including surgery, radiation, and hormone therapy, can be used to manage and treat DCIS effectively. Treatment for invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) in Chennai can be more complex as the cancer has spread beyond the ducts into surrounding tissues.
Here are the common treatment options:
- Surgery: As mentioned above, surgery such as lumpectomy or mastectomy is often the first line of treatment.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation is often recommended after a lumpectomy to destroy any remaining cancer cells. It may also be used in some cases of non-invasive breast cancer in Chennai.
- Hormone Therapy: If the DCIS tumor is hormone receptor-positive, hormone therapy may be used to reduce the risk of recurrence. This treatment blocks the hormones that promote cancer growth.
- Chemotherapy: For more advanced or invasive types of breast cancer like invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) in Chennai, chemotherapy may be suggested to destroy any remaining cancer cells or to shrink the tumor before surgery.
Risk Factors for Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS)
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Understanding these risk factors can help with early detection and prevention, as well as making informed choices about ductal carcinoma in situ treatment in chennai.
- Age: Women over the age of 50 are more commonly diagnosed with DCIS. As women age, the risk of developing non-invasive breast cancer increases.
- Family History: Having a family history of breast cancer, particularly if a close relative has been diagnosed, significantly raises your risk of developing DCIS or other types of breast cancer.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Prolonged use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT), particularly estrogen-based therapies, can elevate the risk of DCIS. This is due to the hormonal influence on breast tissue.
- Radiation Exposure: Previous exposure to radiation, particularly to the chest area for other medical treatments, increases the likelihood of developing DCIS later in life.
- Early Menstruation/Late Menopause: Women who began menstruating at an early age or experienced menopause later in life have extended exposure to estrogen, increasing their risk of DCIS and other breast cancers.
These risk factors, while not controllable in many cases, highlight the importance of regular screenings and vigilance, especially for those at higher risk of ductal carcinoma in situ symptoms.
Prevention of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS)
Although preventing ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) entirely may not be possible, certain lifestyle changes and preventive measures can significantly reduce your risk. Implementing these strategies can help with early detection and reduce the likelihood of developing non-invasive breast cancer.
- Routine Screenings: Regular mammograms and breast self-exams are critical for catching ductal carcinoma in situ symptoms in chennai early. Routine screenings are particularly important for women over 40 or those with a family history of breast cancer.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, reducing alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking can lower your risk of DCIS and other forms of breast cancer.
- Limit Hormone Therapy: If possible, limit or avoid the use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT), especially long-term use, as it increases the risk of developing ductal carcinoma in situ treatment in chennai. Consult with your doctor about alternatives to HRT.
- Breastfeeding: Women who breastfeed for extended periods may experience a reduced risk of breast cancer. The hormonal changes associated with breastfeeding can help protect against the development of non-invasive breast cancer.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your lifestyle, you can significantly reduce your risk of DCIS and ensure that early detection leads to better outcomes in ductal carcinoma in situ treatment in chennai.
DCIS Diagnosed with Invasive Breast Cancer
In some cases, DCIS may coexist with invasive breast cancer. The treatment approach includes:
- Surgical Options:
- Lumpectomy: Removing the affected area while preserving the breast.
- Mastectomy: Complete removal of one or both breasts if DCIS is extensive or accompanied by invasive cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: Often recommended post-lumpectomy to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Necessary if invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) in chennai is present and has spread to lymph nodes or beyond.
- Targeted Therapy: For HER2-positive cancers, drugs like Trastuzumab are highly effective.
Combining these treatments ensures comprehensive management of both DCIS and invasive components.
Why Early Detection of DCIS is Critical
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) is classified as a non-invasive breast cancer, meaning it remains confined to the milk ducts and hasn’t spread to surrounding tissues. However, if left untreated, DCIS can progress into invasive breast cancer, which significantly increases health risks and complicates treatment options.
Early detection through regular mammograms is essential, especially for women with a family history of breast cancer or other risk factors. Catching ductal carcinoma in situ symptoms in chennai early allows for more effective ductal carcinoma in situ treatment in chennai and helps prevent the condition from progressing into invasive cancer. Routine screenings offer the best chance of detecting DCIS when it’s most treatable.
Recovery and Monitoring
After completing ductal carcinoma in situ treatment, consistent monitoring is crucial to ensure the cancer does not recur or evolve into invasive forms. Follow-up mammograms are typically recommended every 6 to 12 months, based on individual risk factors. In addition to medical checkups, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, performing regular self-breast exams, and promptly addressing any new symptoms with your healthcare provider are essential aspects of long-term post-treatment care.
How is DCIS Diagnosed?
Early and accurate diagnosis of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) in chennai is essential for determining the most appropriate treatment plan. Diagnostic methods include:
- Mammograms: The primary tool for detecting DCIS, often revealing microcalcifications indicative of the condition.
- Breast Ultrasound: Used to examine suspicious areas further and differentiate DCIS from other abnormalities.
- Biopsy Procedures: Core needle biopsy or stereotactic biopsy helps confirm the diagnosis by analyzing tissue samples.
- MRI Scans: Recommended for high-risk individuals to assess the extent of DCIS more precisely.
Early detection of DCIS symptoms, such as abnormal nipple discharge or changes in breast tissue, plays a vital role in successful treatment.
Moving On After DCIS
Life after a DCIS diagnosis involves managing physical and emotional recovery. Here’s how patients can transition effectively:
- Follow-Up Care: Regular screenings and follow-ups ensure that there is no recurrence or progression to invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC).
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including balanced nutrition and regular exercise, supports overall well-being.
- Psychological Support: Joining support groups or seeking counseling can help patients cope with the emotional aspects of a cancer diagnosis.
- Hormonal Therapy: For hormone receptor-positive cases, medications like Tamoxifen can reduce the risk of recurrence.
Many patients find reassurance in knowing that DCIS, being non-invasive breast cancer, has excellent treatment outcomes when addressed promptly.
What Are the Surgical Procedures Available for Ductal Carcinoma
When diagnosed with Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS), treatment options are carefully chosen based on the patient’s condition and the severity of the disease. There are several surgical procedures available to address Ductal Carcinoma in Situ treatment in Chennai, which are designed to remove the abnormal cells and ensure they do not progress into invasive cancer.
- Lumpectomy: This is the most common procedure for DCIS. During this surgery, the surgeon removes the tumor along with a small margin of surrounding healthy tissue. The goal is to conserve as much of the breast tissue as possible while ensuring all abnormal cells are removed.
- Mastectomy: In cases where DCIS is more widespread or there are multiple areas of concern, a mastectomy may be recommended. This procedure involves removing the entire breast tissue. There are two types of mastectomy:
- Total Mastectomy: Removal of the entire breast.
- Skin-Sparing Mastectomy: Removal of the breast tissue but leaving the skin intact, allowing for reconstruction.
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: For some cases of non-invasive breast cancer in Chennai, your doctor may perform a sentinel lymph node biopsy to check if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. This involves removing a few of the lymph nodes closest to the tumor and testing them for cancer cells.
Conclusion
DCIS is a highly treatable condition when caught early. Understanding your options for Ductal Carcinoma in Situ treatment allows for informed decision-making and peace of mind. Whether through surgery, radiation, or hormonal therapy, managing DCIS effectively can significantly reduce the risk of future complications. Early detection through routine screenings and being aware of ductal carcinoma in situ symptoms in chennai are vital steps in safeguarding your health.